Digitalization has become an integral part of our daily lives, transforming the way we live, work, and interact. From using smartphones to access information and communicate with others to relying on digital platforms for shopping, banking, and entertainment, the impact of digitalization is undeniable. But what does digitalization really mean? It refers to the process of converting analog information into digital form, making it more accessible, efficient, and convenient. In this article, we explore the various aspects of digitalization in our daily lives and how it has revolutionized the way we carry out everyday tasks. Digitalization refers to the process of using digital technology to transform various aspects of everyday life. It involves the conversion of analog information or processes into digital formats, enabling easier storage, access, and manipulation of data. Digitalization has significantly impacted numerous areas of daily life, ranging from communication and entertainment to finance and education. This article will explore the definition of digitalization, its impact on various aspects of daily life, its advantages and disadvantages, as well as the future trends and outlook in this digital era.

This image is property of i.ytimg.com.
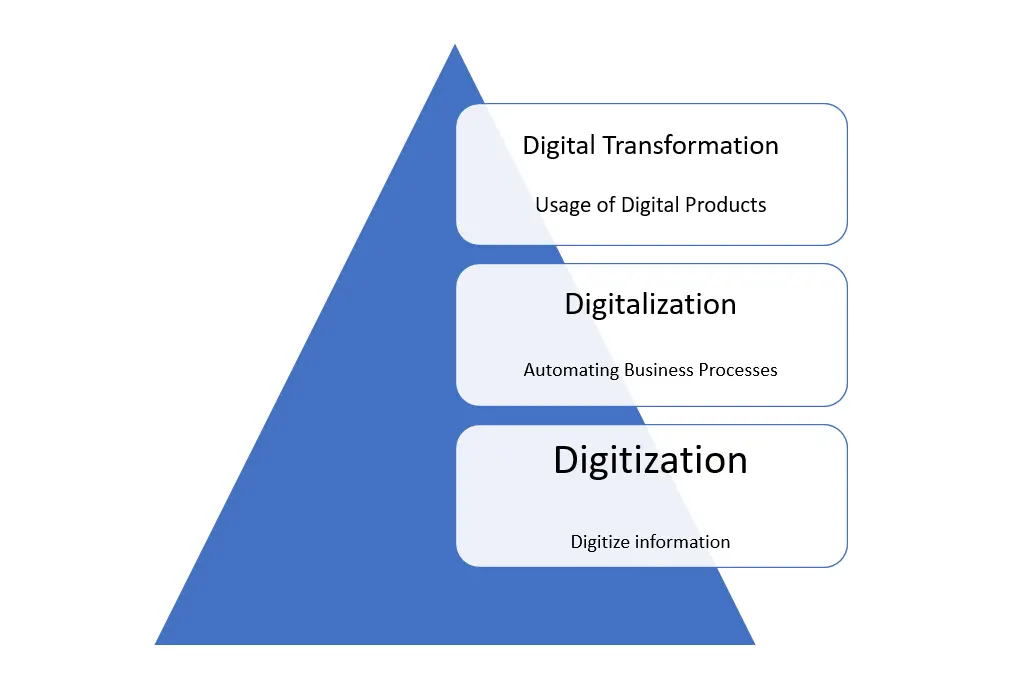
The Definition of Digitalization
Understanding Digitalization
Digitalization is the integration of digital technology into various spheres of life, changing the way people interact, communicate, and conduct everyday activities. It involves the adoption of digital tools, systems, and processes to replace traditional analog methods. By digitizing information, tasks become more efficient, accessible, and user-friendly. Digitalization has become increasingly prevalent due to advancements in technology and the widespread availability of digital devices such as smartphones, computers, and the internet.
Digital Transformation vs Digitalization
Although the terms “digital transformation” and “digitalization” are often used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings. Digital transformation refers to the comprehensive reimagining of an organization’s processes, products, and services using digital technology to drive innovation, growth, and efficiency. It involves significant changes in the company’s business model and overall strategy. On the other hand, digitalization focuses on the specific digitization of various aspects of daily life, enabling individuals to benefit from the use of digital tools and technologies. Digitalization is more personal and consumer-centric, enhancing the way people live, work, and interact in their daily lives.
Impact of Digitalization in Daily Life
Communication and Networking
Digitalization has revolutionized communication, making it faster, more efficient, and more accessible. Through various digital platforms such as social media, messaging apps, and email, people can connect with individuals from all around the world instantly. Video calls and conferences enable face-to-face interactions, even when physical distance separates people. The ease of communication has strengthened personal and professional relationships and facilitated global collaboration.
Entertainment and Media Consumption
Digitalization has transformed the entertainment and media industry. With the rise of streaming services such as Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon Prime Video, people can access a wide range of movies, TV shows, and documentaries at their convenience. Music streaming platforms like Spotify and Apple Music provide instant access to millions of songs. Digital media has made content more accessible and personalized, catering to individual preferences and interests. Additionally, social media platforms have become a source of entertainment, offering a diverse array of user-generated content.
Personal Finance and Banking
Digitalization has greatly influenced personal finance and banking, offering greater convenience, accessibility, and security. Online banking platforms enable individuals to manage their finances, transfer funds, and pay bills from the comfort of their homes. Mobile payment apps, such as PayPal and Venmo, allow for seamless and instant transactions. Digital wallets and contactless payments provide a convenient alternative to carrying physical cash or cards. Furthermore, financial technology (fintech) innovations, such as robo-advisors and budgeting apps, empower individuals to make informed financial decisions and improve their money management skills.
Education and Learning
Digitalization has transformed the education landscape, facilitating remote learning and expanding access to educational resources. Online learning platforms, such as Coursera and Udemy, offer a wide range of courses and certifications that can be accessed from anywhere in the world. Virtual classrooms and video conferencing tools enable students to participate in real-time discussions and interact with teachers and classmates. Educational apps and digital textbooks provide personalized learning experiences, adapting to individual needs and allowing for self-paced learning. Digitalization has made education more flexible, inclusive, and interactive.
E-commerce and Online Shopping
The rise of e-commerce and online shopping is one of the most significant impacts of digitalization. With the convenience of online marketplaces such as Amazon and eBay, individuals can purchase products and services from the comfort of their homes. The availability of customer reviews, detailed product descriptions, and comparison websites empowers consumers to make informed choices. Furthermore, digitalization has given rise to personalized shopping experiences through targeted advertisements and recommendations based on individual preferences. Online shopping has transformed the retail industry, offering convenience, variety, and competitive prices.
Transportation and Travel
Digitalization has revolutionized the transportation and travel industry, making it easier to navigate, plan, and book trips. Ride-hailing services like Uber and Lyft provide convenient and cost-effective alternatives to traditional taxis. Booking platforms like Airbnb and Booking.com offer a vast selection of accommodations worldwide. Online travel agencies enable individuals to compare prices, read reviews, and book flights, hotels, and car rentals with a few clicks. Additionally, digital travel guides and navigation apps provide real-time information, directions, and suggestions, enhancing the overall travel experience.
Healthcare and Wellness
In the healthcare sector, digitalization has brought about numerous benefits, including improved access to medical information, telemedicine services, and health monitoring devices. Online health portals and apps provide reliable medical information, enabling individuals to educate themselves and make informed healthcare decisions. Telemedicine allows for remote consultations with healthcare professionals, especially useful for those in rural or underserved areas. Wearable devices, such as fitness trackers and smartwatches, monitor health metrics and encourage individuals to adopt healthier lifestyles. Digitalization has the potential to streamline healthcare delivery, enhance patient care, and improve health outcomes.
Work and Employment
Digitalization has transformed the way people work and the nature of employment. The rise of remote work and digital collaboration tools has enabled individuals to work from anywhere, improving work-life balance and reducing commuting time. Cloud-based storage and project management systems facilitate easy access and sharing of documents and files. Online freelancing platforms like Upwork and Fiverr connect freelancers with job opportunities globally. Digitalization has also led to the automation of certain tasks through the use of artificial intelligence and robots, augmenting productivity and efficiency in the workplace.
Government and Public Services
Digitalization has impacted government and public services by streamlining administrative processes, increasing transparency, and improving citizen engagement. Online portals and mobile applications allow citizens to access governmental services, file taxes, and renew documents without the need for physical visits. E-government initiatives aim to digitize and automate government procedures, reducing bureaucracy, and enhancing efficiency. Digitalization also enables governments to gather and analyze data for evidence-based decision-making and policy formulation. Furthermore, social media platforms provide channels for citizens to interact directly with government officials, fostering public participation and accountability.
Home and Households
Digitalization has extended into people’s homes, transforming everyday routines and household management. Smart home devices and voice assistants, such as Amazon Echo and Google Home, enable individuals to control lighting, temperature, and appliances using voice commands. Home automation systems provide increased security and energy efficiency. Internet-connected devices like smart TVs and smart refrigerators offer enhanced functionalities and connectivity. Digital parenting tools allow parents to monitor and manage their children’s activities online. Digitalization has made homes more intelligent, interconnected, and efficient.

This image is property of i.ytimg.com.
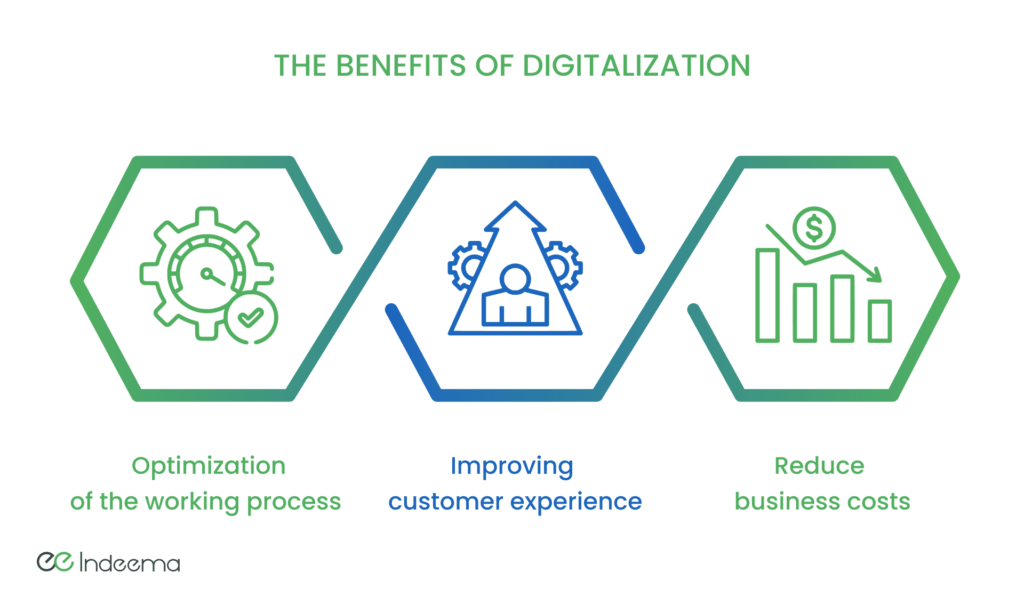
Advantages of Digitalization in Daily Life
Increased Convenience and Efficiency
One of the key advantages of digitalization in daily life is the increased convenience and efficiency it offers. Tasks that previously required physical visits or manual processes can now be completed online with just a few clicks. Whether it’s banking transactions, shopping, or accessing services, digitalization eliminates the need for time-consuming and often inconvenient tasks.
Enhanced Access to Information
Digitalization provides individuals with easy access to a vast amount of information. Online search engines, databases, and digital libraries enable quick and effortless research. Moreover, online platforms and forums connect people with similar interests, making knowledge and expertise readily available to all.
Improved Communication and Collaboration
Digitalization has revolutionized communication and collaboration. Instant messaging apps and video conferencing tools allow for real-time communication, transcending geographical boundaries. Collaborative platforms and cloud storage systems enable individuals to work together on projects, sharing and editing documents simultaneously.
Streamlined Transactions and Financial Management
Digitalization has streamlined transactions and financial management. Online banking and mobile payment apps enable individuals to manage their finances conveniently and securely. Automated bill payments and budgeting apps simplify financial processes, helping individuals stay organized and in control of their money.
Time-Saving and Productivity Boost
Digitalization saves time and enhances productivity by automating repetitive tasks and providing efficient tools and systems. From automated email sorting and document templates to project management software, digital tools enable individuals to focus on high-value tasks, resulting in increased productivity and work efficiency.
Customization and Personalization
Digitalization offers customization and personalization. Online platforms and apps utilize user data and preferences to provide personalized recommendations, from entertainment content to shopping suggestions. Tailored experiences enhance user satisfaction and cater to individual preferences.
Greater Opportunities and Options
Digitalization expands opportunities and options in various aspects of life. Online learning platforms offer a plethora of courses and certifications, allowing individuals to gain knowledge and skills at their own pace. E-commerce platforms provide access to a wide range of products and services, including those not available locally.
Simplified Administrative Processes
Digitalization simplifies administrative processes in various areas, such as government services and healthcare. Online portals and applications reduce paperwork, eliminate the need for physical visits, and speed up bureaucratic processes, enhancing efficiency and reducing administrative burdens.
Remote Access and Remote Work
Digitalization enables remote access to information and services. Individuals can work, learn, and access entertainment from anywhere with an internet connection. Remote work opportunities have increased, allowing individuals to have more flexibility and work-life balance.
Automation and Artificial Intelligence
Digitalization has led to automation and the integration of artificial intelligence in various industries. Automation replaces repetitive tasks, freeing up human resources for more complex and creative work. Artificial intelligence technology improves efficiency and accuracy, leading to advancements in healthcare, manufacturing, and customer service.

This image is property of i.ytimg.com.
Challenges and Concerns of Digitalization
Digital Divide and Inequality
Despite the widespread impact of digitalization, a digital divide persists, leading to inequality. Not everyone has equal access to digital tools and the internet, creating barriers to opportunities and resources. This divide disproportionately affects marginalized communities and individuals in rural or remote areas.
Privacy and Security Risks
Digitalization raises concerns about privacy and cybersecurity. With an increasing amount of personal data being stored and shared online, individuals face the risk of data breaches, identity theft, and unauthorized access. It is crucial to implement robust security measures and regulations to protect sensitive information and maintain trust in digital systems.
Technological Dependence and Addiction
Digitalization has led to increased reliance on technology, potentially resulting in technological dependence and addiction. Excessive use of digital devices and platforms can lead to psychological and social issues, such as decreased attention span, decreased physical activity, and social isolation. Striking a balance between digital engagement and offline activities is essential for healthy lifestyles.
Disconnection and Impersonal Interactions
While digitalization facilitates communication, it can also lead to disconnection and impersonal interactions. Digital communications lack physical presence, non-verbal cues, and personal touch, potentially affecting the quality of relationships. It is crucial to maintain face-to-face interactions and strike a balance between digital and in-person connections.
Job Displacement and Skills Gap
Digitalization and automation raise concerns about job displacement and the widening skills gap. As tasks become automated, certain job roles may become obsolete, requiring individuals to adapt and acquire new skills. Ensuring adequate training and education programs can help individuals stay relevant in the changing digital landscape.
Data and Information Overload
Digitalization has led to an overwhelming amount of data and information. The ease of accessing information and the constant influx of content can lead to information overload and cognitive overload. Developing information literacy skills and employing effective information filtering techniques are essential to navigate the digital world effectively.
Cybercrime and Fraud
With increased digitalization, the risk of cybercrime and online fraud has also risen. Malicious individuals and organizations exploit vulnerabilities in digital systems to gain unauthorized access to personal and financial information. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures and educating individuals about online safety can help mitigate these risks.
Digital Exhaustion and Burnout
Constant exposure to digital devices and platforms can lead to digital exhaustion and burnout. The pressure to be constantly connected and available, combined with information overload, can take a toll on mental and emotional well-being. It is important to practice digital detox, set boundaries, and employ self-care strategies to prevent digital overload.
Ethical and Legal Issues
Digitalization raises ethical and legal concerns regarding data privacy, surveillance, and the potential misuse of technology. The collection and analysis of personal data raise questions about consent, transparency, and accountability. Establishing comprehensive legal frameworks and ethical guidelines is essential to protect individual rights and ensure responsible use of digital technology.
Environmental Impact
Digitalization has an environmental impact, particularly in terms of energy consumption and electronic waste. The increased demand for digital infrastructure and devices leads to higher energy consumption and carbon emissions. Additionally, the disposal of electronic waste poses environmental challenges. Developing sustainable digital solutions and promoting responsible e-waste management are essential for mitigating these impacts.

This image is property of blogger.googleusercontent.com.
Digitalization Trends and Future Outlook
Internet of Things (IoT) and Smart Devices
The Internet of Things (IoT) and smart devices represent a growing trend in digitalization. IoT connects everyday objects to the internet, enabling data exchange and automation. Smart devices, such as smart home appliances and wearable gadgets, enhance convenience and interconnectivity, shaping the future of daily life.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning are poised to revolutionize various industries. AI-powered systems have the ability to analyze vast amounts of data, make predictions, and perform complex tasks. Machine learning algorithms continuously improve their performance based on experience, leading to advancements in healthcare, finance, transportation, and more.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology, known for its application in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, has the potential to transform various sectors. Blockchain provides a decentralized and transparent system for recording transactions and storing data securely. It can enhance supply chain management, improve transparency in governance, and facilitate secure digital identities.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) technologies offer immersive and interactive experiences, impacting industries such as gaming, entertainment, education, and healthcare. AR overlays digital information onto the real world, while VR creates entirely virtual environments, opening up new possibilities for communication, learning, and entertainment.
Cloud Computing and Edge Computing
Cloud computing allows for the storage and access of data through remote servers, enabling flexibility and scalability. Edge computing brings computing power closer to the source of data and reduces latency, facilitating real-time processing and analysis. Both technologies are crucial for supporting the increasing demand for data-intensive applications and services.
5G Network and Connectivity
The deployment of 5G networks promises faster and more reliable internet connectivity, enabling seamless streaming, real-time communication, and IoT applications. 5G networks will accelerate the digitalization of various industries, including healthcare, transportation, and smart cities, by providing high-speed, low-latency connections.
Data Analytics and Data-driven Insights
Data analytics plays a crucial role in digitalization, allowing for the extraction of valuable insights and patterns from large datasets. Data-driven decision-making empowers organizations and individuals to make informed choices, optimize processes, and drive innovation. Advancements in data analytics techniques are poised to transform various sectors, ranging from healthcare to finance.
Cybersecurity and Privacy Solutions
As digitalization expands, so does the need for robust cybersecurity and privacy solutions. Innovations in encryption, biometrics, and authentication technologies are key to safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining trust in digital systems. Continued investment in cybersecurity measures is crucial to stay ahead of evolving threats.
Digital Health and Telemedicine
Digitalization in healthcare, known as digital health or e-health, involves the use of digital technologies to improve healthcare delivery, diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring. Telemedicine enables remote consultations, reducing the need for physical visits and improving access to healthcare, especially in underserved areas. Digital health solutions have the potential to enhance patient care, improve public health outcomes, and increase efficiency in healthcare systems.
Sustainable and Green Technologies
In response to the environmental challenges posed by digitalization, sustainable and green technologies are gaining momentum. Initiatives such as renewable energy sources to power digital infrastructure and the development of eco-friendly electronic devices aim to reduce energy consumption and minimize electronic waste. Incorporating sustainability principles into digitalization strategies is essential to ensure a greener future.
In conclusion, digitalization has reshaped various aspects of daily life, creating opportunities for increased convenience, enhanced communication, and improved accessibility. However, it also presents challenges such as privacy risks, inequality, and environmental impact. Understanding the impact, advantages, and challenges of digitalization is crucial for effectively navigating the digital landscape and harnessing its potential for a better future. As technology continues to advance, staying updated with digitalization trends and proactively addressing concerns is essential for ensuring a balanced and inclusive digital transformation.

This image is property of i.ytimg.com.














.webp?width=945&height=500&name=Digital%20Transformation%20Challenge%20(1).webp)