So, you’ve heard the term “digital transformation” being thrown around a lot lately, but you’re not quite sure what it actually entails. Well, no worries my friend, I’ve got you covered. In this article, we’ll be taking a closer look at the four main areas of digital transformation and how they are revolutionizing the way businesses operate in the modern age. From embracing new technologies to reimagining customer experiences, buckle up as we unravel the secrets to thriving in the digital era.
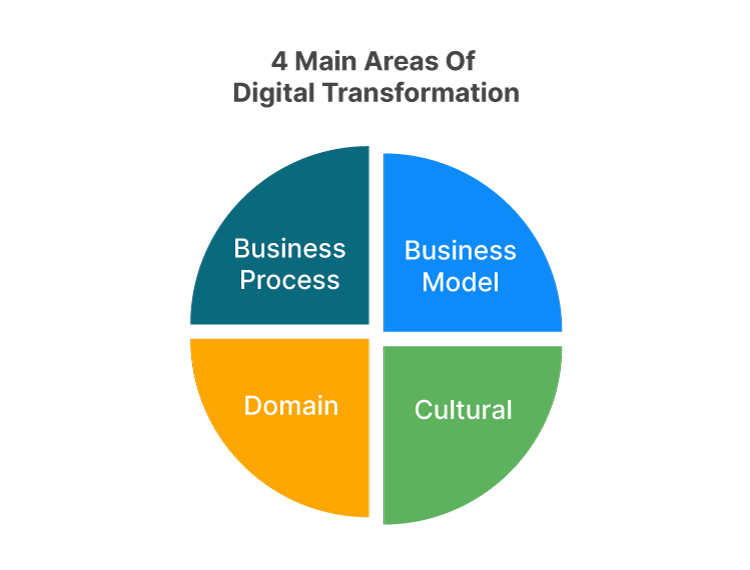
This image is property of magenest.com.
1. Strategy and Leadership
1.1 Digital Strategy
Digital strategy is a crucial component of any successful digital transformation. It involves developing a clear roadmap for leveraging digital technologies to achieve business objectives. A strong digital strategy outlines the specific goals, target audiences, and desired outcomes of a company’s digital initiatives. It considers factors such as market trends, competitor analysis, and customer needs to identify opportunities for digital innovation. By defining a comprehensive digital strategy, organizations can align their resources and efforts towards creating a competitive advantage in the digital landscape.
1.2 Leadership and Culture
Digital transformation requires strong leadership and a supportive organizational culture. Leaders play a vital role in driving change and fostering a digital mindset within the company. They need to inspire and motivate employees towards embracing new technologies and innovative ways of working. Effective leaders also prioritize continuous learning and provide the necessary resources for upskilling and reskilling the workforce. Furthermore, cultivating a culture that embraces experimentation, collaboration, and agility is essential for successful digital transformation. Organizations that prioritize leadership development and foster a digital-friendly culture are better equipped to navigate the complexities of the digital age.
1.3 Organizational Readiness
Organizational readiness refers to the preparedness of a company to undergo digital transformation. It involves evaluating the current state of the organization, including its infrastructure, processes, and capabilities, to identify any gaps or barriers that may hinder digital initiatives. Assessing the readiness of the workforce is also crucial, as employees need the right skills and knowledge to effectively leverage digital technologies. By conducting a thorough assessment of organizational readiness, companies can develop targeted strategies to address gaps and ensure a smooth transition towards becoming digitally mature.
1.4 Change Management
Change management is a critical aspect of digital transformation. It involves effectively managing the people side of change to ensure successful adoption and utilization of new digital technologies. Change management practices include communication, training, and providing ongoing support to employees throughout the transformation process. It is important to create a sense of urgency, establish clear goals, and involve employees in the decision-making process to minimize resistance and enhance acceptance of change. By implementing robust change management strategies, organizations can navigate the challenges associated with digital transformation and maximize the benefits of technological innovation.
2. Customer Experience
2.1 Omni-channel Experience
The omni-channel experience focuses on providing a seamless and consistent customer journey across multiple channels, both online and offline. In today’s digital age, customers interact with businesses through various touchpoints such as websites, mobile apps, social media, and physical stores. An omni-channel approach ensures that every interaction is interconnected and offers a personalized experience. By integrating data and leveraging digital tools, organizations can better understand customer preferences and deliver relevant and timely experiences. This, in turn, enhances customer satisfaction, loyalty, and advocacy, laying the foundation for long-term business success.
2.2 Personalization and Customization
Personalization and customization are key drivers of enhanced customer experiences. By leveraging data analytics and artificial intelligence, organizations can gather insights about customer behavior, preferences, and purchase history to offer tailored recommendations and personalized marketing messages. Personalization goes beyond simply addressing customers by their names; it involves anticipating their needs and providing relevant content, products, and services. Customization, on the other hand, focuses on allowing customers to actively participate in the design or configuration of products and services to better align with their individual preferences. Both personalization and customization contribute to customer satisfaction, loyalty, and ultimately, business growth.
2.3 Customer Journey Mapping
Customer journey mapping involves visualizing and understanding the entire lifecycle of a customer, from their initial awareness of a product or service to post-purchase interactions. It helps organizations identify touchpoints, pain points, and opportunities for improvement along the customer journey. By mapping out the customer journey, businesses gain valuable insights into customer motivations, expectations, and emotions at each stage. This understanding allows for targeted interventions to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. Customer journey mapping also highlights areas where digital technologies can be leveraged to streamline processes, automate tasks, and offer personalized experiences.
2.4 Voice of the Customer
The voice of the customer (VoC) refers to the feedback, opinions, and preferences of customers. Collecting and analyzing the VoC is essential for understanding customer needs and expectations. Through surveys, interviews, social media monitoring, and other feedback channels, organizations can gather valuable insights that can drive product and service improvements. The VoC also helps companies identify emerging trends, anticipate customer demands, and make data-driven decisions. By actively listening to the voice of the customer, organizations can continuously improve their offerings and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
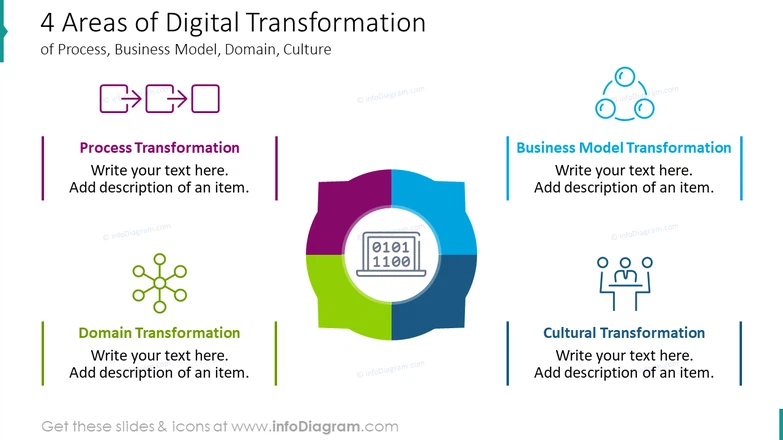
This image is property of cdn.infodiagram.com.
3. Operations and Processes
3.1 Agile Methodologies
Agile methodologies are widely adopted in digital transformation initiatives to enhance operational efficiency and foster innovation. Agile principles emphasize iterative, collaborative, and adaptive approaches to project management and product development. By breaking down projects into smaller, manageable tasks and incorporating feedback loops, organizations can respond quickly to changing market demands and customer needs. The use of agile methodologies also promotes cross-functional collaboration and teamwork, enabling faster decision-making and problem-solving. Implementing agile practices empowers organizations to accelerate time to market, improve product quality, and drive continuous improvement.
3.2 Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics play a crucial role in streamlining operations and optimizing processes. Automation involves the use of software and technology to automate repetitive and manual tasks, reducing human error and increasing efficiency. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) takes automation a step further by employing software bots to mimic human interactions with systems and applications. RPA can handle complex tasks, improve accuracy, and free up employees to focus on higher-value activities. Adopting automation and robotics not only improves operational productivity but also enables organizations to allocate resources strategically and drive cost savings.
3.3 Data-driven Decision Making
Data-driven decision making relies on the analysis of large volumes of data to inform strategic choices and operational decision-making. Organizations can leverage data analytics tools and technologies to collect, analyze, and interpret data from various sources. By harnessing the power of data, companies gain insights into customer behavior, market trends, and operational performance. These insights enable informed decision-making, enhance forecasting accuracy, and drive strategy execution. Moreover, data-driven decision making fosters a culture of experimentation and innovation, as it allows organizations to test hypotheses, measure outcomes, and make data-backed adjustments.
3.4 Supply Chain Optimization
Digital transformation has a significant impact on supply chain management, enabling organizations to optimize processes and improve efficiency. By leveraging technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence, and cloud computing, companies can gain real-time visibility into their supply chain operations. This visibility helps identify potential bottlenecks, delays, and inefficiencies, allowing organizations to proactively address them. Supply chain optimization also involves automating manual tasks, enhancing collaboration with suppliers and partners, and using advanced analytics to predict demand, optimize inventory levels, and reduce costs. Improved supply chain visibility and efficiency contribute to shorter lead times, improved customer satisfaction, and increased profitability.

This image is property of miro.medium.com.
4. Technology and Innovation
4.1 Cloud Computing
Cloud computing enables organizations to access and store data and applications over the internet, eliminating the need for on-premises infrastructure. It offers scalability, flexibility, and cost savings, as companies can quickly adjust their computing resources based on demand. Cloud computing also fosters collaboration by enabling employees to share and access information from anywhere, at any time. Organizations can leverage cloud-based platforms and services to drive innovation, streamline operations, and enhance business continuity. The adoption of cloud computing enables companies to focus on their core competencies while relying on reliable and secure infrastructure.
4.2 Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the interconnected network of physical devices, vehicles, appliances, and other objects that collect and exchange data over the internet. IoT enables organizations to gather real-time data from various sources, enabling better decision-making and process optimization. In industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and agriculture, IoT enables monitoring, predictive maintenance, and improved resource allocation. IoT also enhances customer experiences by enabling smart homes, wearable devices, and connected cars. Embracing IoT technologies allows organizations to create innovative products and services, improve operational efficiency, and generate new revenue streams.
4.3 Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning are transforming industries by enabling machines to simulate intelligent human behavior and learn from experience. AI technologies such as natural language processing and computer vision enable automation and augmentation of tasks previously performed by humans. Machine Learning algorithms analyze large datasets to derive insights, make predictions, and improve accuracy over time. AI and Machine Learning have applications in various domains, including customer service, fraud detection, personalized marketing, and supply chain optimization. Embracing AI and Machine Learning enables organizations to unlock the potential of big data, improve decision-making, and enhance operational efficiency.
4.4 Cybersecurity and Data Privacy
As organizations increasingly rely on digital technologies, the importance of cybersecurity and data privacy becomes paramount. Cybersecurity measures protect digital assets, networks, and data from unauthorized access, disruption, and theft. Organizations need to implement robust security measures, including firewalls, encryption, and access controls, to safeguard their digital infrastructure. Data privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), require organizations to handle personal data responsibly and transparently. Compliance with data privacy regulations ensures customer trust and protects organizations from reputational and financial risks. Prioritizing cybersecurity and data privacy allows organizations to build a secure and resilient digital ecosystem for their customers and stakeholders.
In conclusion, digital transformation encompasses a comprehensive and interconnected set of areas that organizations need to address to stay competitive in the digital age. Strategy and leadership set the direction and build the culture necessary for successful digital initiatives. Customer experience is optimized by providing seamless omni-channel experiences, personalization, and using customer journey mapping. Operations and processes are transformed by adopting agile methodologies, automation, data-driven decision making, and optimizing the supply chain. Finally, technology and innovation play a pivotal role in unleashing the potential of cloud computing, IoT, AI and Machine Learning, and ensuring cybersecurity and data privacy. By focusing on these four main areas of digital transformation, organizations can adapt, innovate, and thrive in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
This image is property of miro.medium.com.
