In today’s fast-paced world, digitalization has become an integral part of how businesses operate. From streamlining processes to connecting with customers, the impact of digitalization on the face of business is undeniable. With the rise of technology and the increasing popularity of online platforms, businesses are now able to reach a wider audience, optimize their operations, and stay ahead in an ever-evolving market. In this article, we will explore the various ways in which digitalization is reshaping the business landscape and the opportunities it presents for both established companies and aspiring entrepreneurs. So, fasten your seatbelts and get ready to embark on a journey into the exciting world of digital transformation.
1. Transformation in Communication
1.1 Increased Connectivity
Digitalization has revolutionized communication by increasing connectivity on a global scale. With the advent of the internet, it is now possible to connect with people and businesses around the world with just a few clicks. This increased connectivity has opened up new opportunities for businesses to expand their reach and engage with customers in ways that were previously unimaginable.
1.2 Effortless Communication
Digitalization has made communication faster, easier, and more efficient than ever before. With tools such as email, instant messaging, and video conferencing, you can now communicate with colleagues, clients, and customers in real-time, no matter where they are located. This has eliminated the barriers of time and distance, allowing for seamless communication and collaboration.
1.3 Easier Collaboration
Digitalization has brought about a shift in how businesses collaborate. With cloud-based platforms and project management tools, teams can now work together on documents, share information, and track progress in real-time. This has streamlined the collaboration process, making it easier to work with colleagues and external partners, leading to increased productivity and improved outcomes.
2. Evolution of Marketing Strategies
2.1 Targeted Advertising
Digitalization has transformed marketing strategies by allowing businesses to target their advertising efforts with precision. Through data analytics and online tracking, businesses can gather insights about their target audience’s demographics, preferences, and behaviors. This data can then be used to create tailored marketing campaigns that resonate with specific segments of the population, increasing the chances of conversion and ROI.
2.2 Personalized Marketing
Gone are the days of one-size-fits-all marketing messages. Digitalization has enabled businesses to personalize their marketing efforts, ensuring that each customer receives relevant and customized content. By leveraging customer data and utilizing marketing automation tools, businesses can deliver personalized experiences and recommendations, resulting in increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
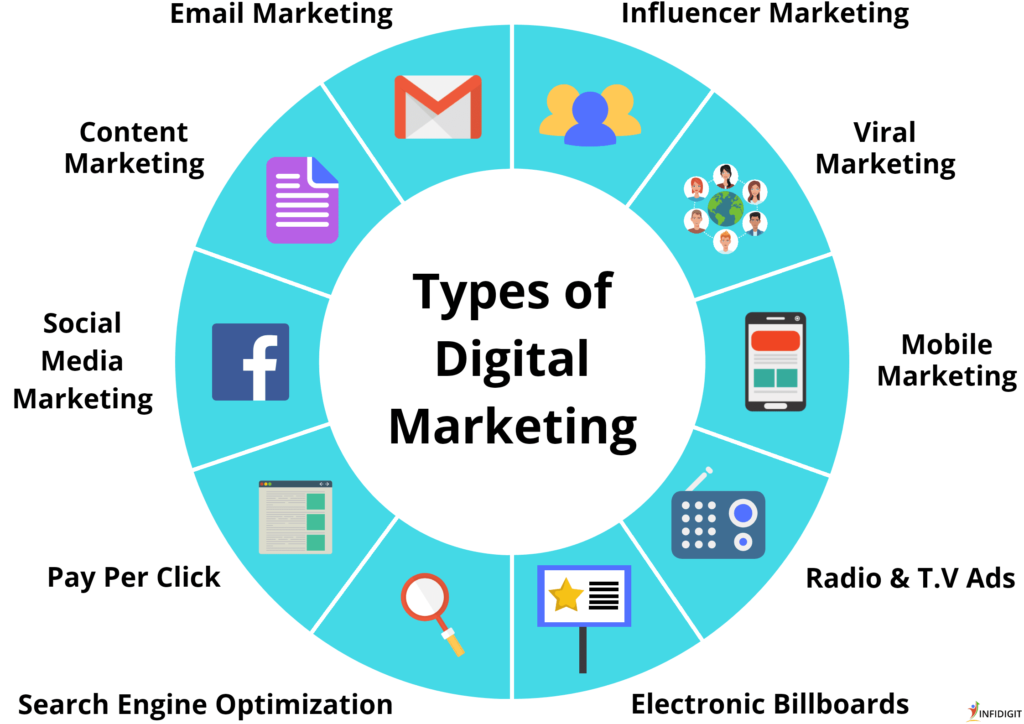
2.3 Social Media Engagement
Digitalization has propelled the rise of social media, creating new avenues for businesses to engage with their customers. Platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter provide businesses with the opportunity to interact directly with their target audience, build brand awareness, and foster customer loyalty. Through social media, businesses can share content, run promotional campaigns, and gather valuable feedback, ultimately driving sales and enhancing brand reputation.

This image is property of www.aeologic.com.
3. Streamlining Business Operations
3.1 Automation of Processes
Digitalization has paved the way for automation of various business processes, leading to increased efficiency and accuracy. From automating repetitive tasks such as data entry and invoicing to implementing sophisticated robotic process automation (RPA) technologies, businesses can streamline their operations, reduce human error, and allocate their workforce to more strategic and value-added activities.
3.2 Enhanced Efficiency
Digitalization has empowered businesses to optimize their operations and achieve higher levels of efficiency. Through the use of enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, businesses can integrate and automate key functions such as inventory management, supply chain logistics, and financial reporting. This streamlines workflows, improves coordination between departments, and enables real-time data visibility, resulting in cost savings and improved decision-making.
3.3 Cost Reduction
Digitalization has the potential to significantly reduce costs for businesses. By embracing cloud computing, businesses can eliminate the need for costly on-premises infrastructure and hardware, leading to substantial savings in terms of hardware maintenance and energy consumption. Additionally, digital tools enable businesses to reduce the amount of physical paperwork and manual processes, further decreasing operational costs and improving overall profitability.
4. Expanding Market Reach
4.1 Global Market Access
Digitalization has opened doors for businesses to access global markets like never before. With the ability to establish an online presence through websites, e-commerce platforms, and digital marketplaces, businesses can reach customers across borders and continents. This has created unprecedented opportunities for growth and expansion, allowing businesses to tap into new markets and diversify their customer base.
4.2 Online Presence
Having a strong online presence has become crucial for businesses in the digital age. Digitalization has made it essential for businesses to have a website or an e-commerce platform where customers can easily find and interact with them. This online presence enables businesses to showcase their products or services, provide detailed information, and facilitate seamless transactions, ultimately driving sales and enhancing brand visibility.
4.3 Direct-to-Consumer Model
Digitalization has empowered businesses to adopt a direct-to-consumer (DTC) model, bypassing traditional intermediaries and connecting directly with customers. Through e-commerce platforms and social media, businesses can establish direct relationships with consumers, understand their needs and preferences, and provide personalized experiences. This not only strengthens customer loyalty but also allows businesses to capture a larger share of the value chain, resulting in increased profitability.

This image is property of www.whappy.it.
5. Reshaping Customer Experience
5.1 Improved Convenience
Digitalization has transformed the customer experience by making it more convenient than ever before. With the ability to shop online, customers can browse and purchase products or services at any time, from anywhere, without the need to visit physical stores. This convenience factor has led to a significant shift in consumer behavior, with more and more people opting for online shopping for its ease and accessibility.
5.2 Customization and Personalization
Digitalization has revolutionized the way businesses interact with their customers by allowing for customization and personalization of products and services. Through the collection and analysis of customer data, businesses can understand individual preferences and tailor their offerings accordingly. This not only enhances customer satisfaction but also creates a sense of exclusivity, leading to increased brand loyalty and repeat purchases.
5.3 Enhanced Customer Support
Digitalization has revolutionized customer support by providing businesses with various channels to engage with their customers and promptly address their queries or concerns. Through email, live chat, social media, and self-service portals, businesses can provide instant support and assistance, ensuring a seamless customer experience. This responsiveness and availability of support contribute to customer satisfaction and ultimately foster long-term relationships.
6. Harnessing Data and Analytics
6.1 Big Data Analytics
Digitalization has resulted in the generation of vast amounts of data, which can be harnessed for business insights and decision-making through big data analytics. By analyzing structured and unstructured data from various sources, businesses can uncover hidden patterns, identify trends, and gain valuable insights into customer behavior, market dynamics, and operational performance. This data-driven approach enables businesses to make informed decisions, optimize processes, and drive innovation.
6.2 Business Intelligence
Digitalization has made it easier for businesses to collect, store, and analyze data, leading to the emergence of sophisticated business intelligence (BI) tools. These tools allow businesses to transform raw data into meaningful insights, visualizations, and reports, providing stakeholders with a holistic view of the business and enabling data-driven decision-making. With BI, businesses can identify areas of improvement, track key performance indicators (KPIs), and align strategies to achieve their goals.
6.3 Predictive Analysis
Digitalization has given rise to advanced analytics techniques, such as predictive analysis, which leverage historical data and algorithms to forecast future outcomes. By applying predictive models, businesses can anticipate customer behavior, demand patterns, and market trends, allowing them to proactively respond and adapt their strategies. This empowers businesses to stay ahead of the competition, mitigate risks, and maximize opportunities, ultimately driving growth and profitability.

This image is property of www.elegantmicroweb.com.
7. Rise of E-commerce
7.1 Online Shopping Boom
Digitalization has fueled the rapid growth of e-commerce, revolutionizing the retail industry. With the convenience and accessibility of online shopping, consumers can explore a vast array of products, compare prices, and make purchases with just a few clicks. This shift in consumer behavior has compelled businesses to establish robust e-commerce platforms, invest in secure payment systems, and optimize the online shopping experience, driving the growth of the e-commerce industry.
7.2 Mobile Commerce
The proliferation of smartphones and mobile devices has further accelerated the rise of e-commerce through mobile commerce (m-commerce). With mobile apps and optimized mobile websites, businesses can provide a seamless shopping experience on smartphones and tablets. The ubiquity of mobile devices has made it easier for consumers to shop on the go, leading to an increase in mobile transactions and reshaping the way businesses reach and engage with their customers.
7.3 Digital Payment Systems
Digitalization has transformed the way payments are made, with the rise of digital payment systems. Traditional payment methods such as cash and checks have been supplemented by digital alternatives such as mobile wallets, contactless payments, and cryptocurrencies. These digital payment systems offer convenience, security, and speed, allowing businesses to facilitate seamless transactions and eliminate friction points in the purchasing process.
8. Advancements in Supply Chain Management
8.1 Inventory Management
Digitalization has revolutionized inventory management by providing businesses with real-time visibility into their supply chain. Through the use of digital tools such as barcode scanners, RFID tags, and cloud-based inventory management systems, businesses can accurately track inventory levels, monitor stock movements, and optimize replenishment processes. This improves inventory accuracy, reduces stockouts or overstocks, and enhances overall supply chain efficiency.
8.2 Supply Chain Visibility
Digitalization has enabled businesses to achieve transparency and visibility across their supply chain. By leveraging technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, GPS tracking, and cloud-based platforms, businesses can monitor and trace the movement of goods, identify bottlenecks or delays, and proactively manage risks. This enhanced supply chain visibility leads to faster decision-making, better coordination, and improved customer satisfaction.
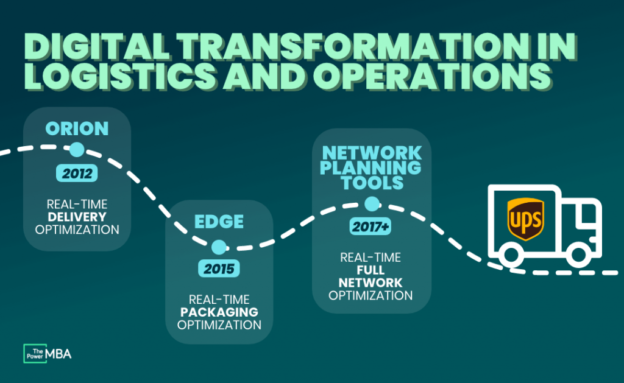
8.3 Real-time Tracking
Digitalization has empowered businesses to track shipments in real-time, offering increased visibility and control over the logistics process. Through GPS-enabled tracking systems and geofencing technology, businesses can monitor the location, condition, and delivery status of their shipments, ensuring timely delivery and minimizing the risk of theft or loss. Real-time tracking enhances supply chain efficiency, reduces lead times, and enhances overall customer satisfaction.

This image is property of www.optimusinfo.com.
9. Cybersecurity Challenges
9.1 Data Breaches and Hacking Threats
As businesses rely more on digital technologies, they face increased cybersecurity risks such as data breaches and hacking threats. Cybercriminals are constantly evolving their tactics to exploit vulnerabilities in digital systems, steal sensitive data, and disrupt operations. Businesses must invest in robust cybersecurity measures, including firewalls, encryption, multi-factor authentication, and employee training, to mitigate these risks and safeguard their valuable assets.
9.2 Protection of Sensitive Information
Digitalization has resulted in the collection and storage of vast amounts of sensitive customer data. This data includes personal information, financial details, and other confidential data that must be protected from unauthorized access or misuse. Businesses must implement strong data protection measures, including secure data storage, regular backups, and compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR or CCPA, to ensure the privacy and trust of their customers.
9.3 Compliance with Privacy Regulations
Digitalization has prompted the introduction of stricter privacy regulations aimed at protecting consumer rights and data privacy. Businesses must comply with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States. Compliance with these regulations involves obtaining consent for data collection, ensuring data security, providing transparency, and respecting individuals’ rights to access, rectify, or delete their personal data.
10. Workforce Transformation
10.1 Remote Workforce
Digitalization has facilitated the rise of remote work, transforming the traditional office-based work model. With digital tools and collaboration platforms, businesses can now enable their employees to work remotely, providing flexibility and work-life balance. Remote work has become especially prevalent in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, allowing businesses to continue operations and adapt to changing circumstances. However, managing and supporting a remote workforce presents new challenges in terms of communication, collaboration, and maintaining productivity.
10.2 Digital Skills Gap
Digitalization has created a demand for new digital skills and competencies in the workforce. Businesses need employees who are proficient in areas such as data analytics, digital marketing, cybersecurity, and emerging technologies. However, there is a growing digital skills gap, with a shortage of workers who possess these skills. Businesses must invest in training and upskilling programs to bridge this gap and ensure a competent and future-ready workforce.
10.3 Automation and Job Displacement
Digitalization brings about automation, which can potentially lead to job displacement. As businesses adopt technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, and process automation, certain roles and tasks may become redundant. However, automation also creates new job opportunities in emerging fields such as data science, AI development, and cybersecurity. Businesses must navigate this transition by reskilling employees, redeploying talent, and fostering a culture of lifelong learning to embrace the benefits of automation while mitigating the impact on workers.
In conclusion, digitalization is transforming the face of business across various aspects. From communication to marketing, operations to customer experience, and workforce to supply chain management, digitalization has brought about significant advancements and opportunities. However, along with the benefits come challenges such as cybersecurity risks, digital skills gap, and job displacement. Businesses must adapt to these changes, embrace digital technologies, and prioritize data-driven decision-making to thrive in the ever-evolving digital landscape.

This image is property of assets.entrepreneur.com.
















.webp?width=945&height=500&name=Digital%20Transformation%20Challenge%20(1).webp)